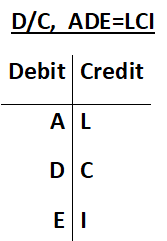
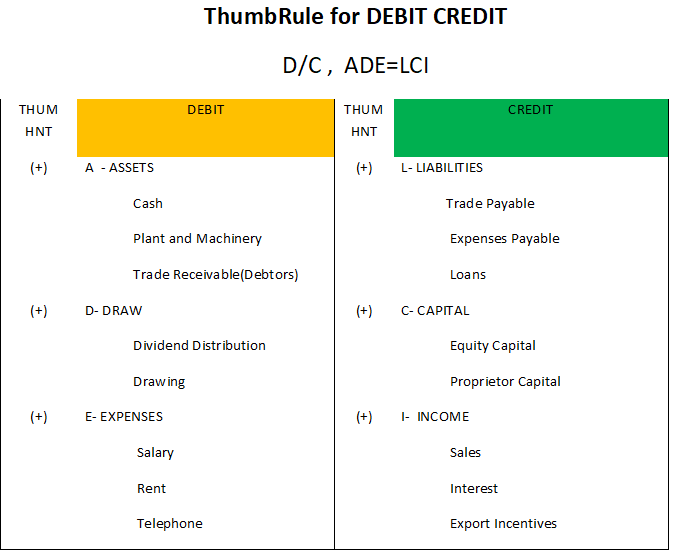
A letter issued by a bank to another bank as a guarantee for payments under the specified contract between the buyers and the sellers.
The issuing bank guarantees that the buyer receiving the payment from the seller in exchange for goods or services will be on time and for the correct amount.
If the seller is not able to make payment against the purchase, the bank will cover the payment amount.
Thus, the real purpose behind issue of letter of credit is to ensure successful business transactions between sellers and buyers. It is an instrument facilitating ease of doing business.
Types of Letter of Credit
There are various types of letter of credit (LC) in the trade transactions viz.
- Commercial Letter of Credit,
- Transferable and Non-Transferable LC,
- Revocable and Irrevocable, Stand-by LC,
- Confirmed & Unconfirmed LC,
- Revolving Letter of Credit,
- Back to Back Letter of Credit,
- Red Clause Letter of Credit,
- Green Clause Letter of Credit,
- At Sight Letter of Credit,
- Deferred Payment Letter of Credit,
Parties to a letter of credit
- Applicant (Purchaser/ importer)
- Issuing bank i.e. importer’s bank which issues the LC
- Beneficiary /Seller exporter