Banking services encompass a wide range of financial products and services provided by banks to individuals, businesses, and institutions. Here’s an overview of the key types of banking services:
| Depositor | Financial Intermediaries | Borrowers |
● Payment services
● Deposit and Lending services
● Investment, pensions, and insurance
● E-banking
PAYMENT SERVICES
Payment services encompass a range of methods and systems that enable individuals and businesses to transfer funds and settle transactions. These services are essential for facilitating commerce, both online and offline. Here’s an overview:
Types of Payment Services
- Traditional Payment Methods:
- Cash: Physical currency used for in-person transactions.
- Checks: Written orders directing a bank to pay a specific amount from the account of the writer.
- Electronic Payment Methods:
- Debit Cards: Linked directly to a bank account, allowing users to spend only what they have.
- Credit Cards: Allow users to borrow funds up to a limit, to be paid back later with interest.
- Prepaid Cards: Loaded with a specific amount of money in advance for spending.
- Online Payment Services:
- Payment Gateways: Facilitate online transactions between customers and merchants (e.g., PayPal, Stripe).
- E-wallets: Digital wallets that store payment information and allow for easy online purchases (e.g., Google Pay, Apple Pay).
- Mobile Payment Solutions:
- Mobile Banking Apps: Allow users to manage bank accounts and make payments through their smartphones.
- Contactless Payments: Enable transactions through NFC technology using smartphones or contactless cards.
- Automated Clearing House (ACH):
- A network for electronically transferring funds between banks, commonly used for direct deposits and bill payments.
DEPOSIT SERVICES AND LENDING SERVICES
Deposit and lending services are core functions of banks and financial institutions. Deposit and lending services are fundamental to the functioning of the banking system and play a crucial role in personal and business finance. Understanding these services helps individuals and businesses make informed financial decisions.
DEPOSIT SERVICES
Deposit services allow customers to place their money in a bank or financial institution for safekeeping, earning interest in the process. Key types include:
- Savings Accounts:
- Definition: Accounts designed to hold funds while earning interest.
- Features: Typically offer lower interest rates, with limited withdrawal options.
- Current Accounts:
- Definition: Transaction accounts primarily for businesses or frequent transactions.
- Features: Usually no interest, with unlimited deposits and withdrawals, often accompanied by check-writing privileges.
- Fixed Deposits (FDs):
- Definition: Accounts where money is deposited for a fixed term at a higher interest rate.
- Features: Early withdrawal may incur penalties; interest rates are typically higher than savings accounts.
- Recurring Deposits (RDs):
- Definition: Accounts that allow customers to deposit a fixed amount regularly.
- Features: Ideal for saving over time, offering a fixed interest rate.
- Money Market Accounts:
- Definition: Hybrid accounts that combine features of savings and checking accounts.
- Features: Typically offer higher interest rates with limited check-writing abilities.
LENDING SERVICES AND BANK CREDIT
Lending services enable banks to provide loans to individuals and businesses, allowing them to borrow funds for various purposes.
- Personal Loans:
- Definition: Unsecured loans for personal use, such as medical expenses or vacations.
- Features: Fixed interest rates and monthly payments; often based on creditworthiness.
- Home Loans (Mortgages):
- Definition: Loans specifically for purchasing real estate.
- Features: Typically secured by the property, with long repayment terms (15-30 years).
- Business Loans:
- Definition: Loans aimed at financing business operations or expansion.
- Features: Can be secured or unsecured, with varying terms based on the business’s financial health.
- Auto Loans:
- Definition: Loans for purchasing vehicles.
- Features: Usually secured by the vehicle itself, with fixed repayment terms.
- Student Loans:
- Definition: Loans to cover educational expenses.
- Features: Often have deferred repayment options until after graduation.
- Payday Loans:
- Definition: Short-term, high-interest loans meant to cover immediate expenses until the next paycheck.
- Features: High fees and interest rates; typically should be avoided unless absolutely necessary.
Bank credit refers to the loans and advances provided by a bank to individuals or companies. These include different types of credit facilities such as:
•Term Loans: These are loans provided for a specific time period and are usually for large capital expenditures.
•Cash Credit: A short-term loan provided to businesses to meet working capital needs. It is usually secured by the company’s inventory or receivables.
•Overdraft: This allows a borrower to withdraw more than what is available in their account, up to a predetermined limit.
•Trade Credit: A credit extended by banks for trade-related purposes, such as import-export financing.
INVESTMENT, PENSIONS, AND INSURANCE SERVICES
Investment, pensions, and insurance services are essential components of financial planning, providing individuals and businesses with tools to manage risks, save for the future, and grow wealth. Here’s an overview of each:
Investment Services
Investment services help individuals and institutions allocate their funds to various assets with the aim of growing wealth over time. Key components include:
- Stocks:
- Definition: Shares of ownership in a company.
- Features: Potential for capital appreciation and dividends; higher risk compared to other investments.
- Bonds:
- Definition: Debt securities issued by corporations or governments.
- Features: Generally considered safer than stocks, providing fixed interest payments and principal repayment at maturity.
- Mutual Funds:
- Definition: Investment vehicles that pool money from multiple investors to buy a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities.
- Features: Managed by professional fund managers; offers diversification and liquidity.
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs):
- Definition: Similar to mutual funds but traded on stock exchanges like individual stocks.
- Features: Typically lower fees and provide flexibility for buying and selling throughout the day.
- Real Estate:
- Definition: Physical properties purchased for rental income or capital appreciation.
- Features: Provides potential for cash flow and tax benefits but involves more management and less liquidity.
- Alternative Investments:
- Definition: Investments outside of traditional asset classes, such as hedge funds, commodities, and collectibles.
- Features: Often used for diversification; may have higher risks and lower liquidity.
Pension Services
Pension services provide retirement income to individuals, helping them save for their post-work life. Key types include:
- Defined Benefit Plans:
- Definition: Employer-sponsored plans that promise a specific payout upon retirement, based on salary and years of service.
- Features: Provides predictable income but relies on employer funding and management.
- Defined Contribution Plans:
- Definition: Retirement plans where employees and/or employers contribute a set amount, with payouts based on investment performance (e.g., 401(k) plans).
- Features: More common today; benefits depend on investment choices and market performance.
- Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs):
- Definition: Personal retirement savings accounts with tax advantages.
- Types: Traditional IRAs (tax-deferred contributions) and Roth IRAs (tax-free withdrawals).
- Annuities:
- Definition: Insurance products that provide regular income payments in exchange for a lump sum payment or series of payments.
- Features: Can be fixed or variable; used for retirement income stability.
Insurance Services
Insurance services protect individuals and businesses from financial losses due to unforeseen events. Key types include:
- Life Insurance:
- Definition: Provides a payout to beneficiaries upon the insured’s death.
- Types: Term life (coverage for a specific period) and whole life (permanent coverage with a cash value component).
- Health Insurance:
- Definition: Covers medical expenses for illnesses, injuries, and other health-related costs.
- Types: Employer-sponsored plans, government programs (e.g., Medicare), and individual plans.
- Property and Casualty Insurance:
- Definition: Protects against loss or damage to property and liability for accidents (e.g., homeowners and auto insurance).
- Features: Covers damages, theft, and liability claims.
- Disability Insurance:
- Definition: Provides income replacement if the insured becomes unable to work due to a disability.
- Features: Short-term and long-term policies are available.
- Liability Insurance:
- Definition: Protects against claims resulting from injuries or damage to other people or property.
- Types: General liability, professional liability (errors and omissions), and product liability.
E-BANKING
E-banking, or electronic banking, refers to the use of digital platforms and technology to manage banking services and conduct financial transactions. It provides customers with a convenient way to access banking services from anywhere, at any time.
Key Features of E-Banking
- Online Account Management:
- Customers can view account balances, transaction history, and statements.
- Users can manage multiple accounts (checking, savings, and loans) from a single interface.
- Fund Transfers:
- Internal Transfers: Move money between accounts within the same bank.
- External Transfers: Send money to accounts at other banks, often through services like NEFT, RTGS, or IMPS.
- Bill Payments:
- Users can pay utility bills, credit card bills, and other payments electronically.
- Scheduled payments can be set up for convenience.
- Mobile Banking:
- Banking apps allow access to services via smartphones or tablets.
- Features include mobile deposits, location-based services, and notifications.
- Online Loan Applications:
- Customers can apply for personal, home, or auto loans online.
- Pre-approval and instant loan status updates are often available.
- Investment Services:
- Access to investment accounts for stocks, mutual funds, and retirement accounts.
- Online trading platforms may also be available.
- Customer Support:
- E-banking platforms typically offer live chat, email support, or FAQs for assistance.
- Automated catboats can provide 24/7 support for common queries.
Benefits of E-Banking
- Convenience: Access banking services 24/7 from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Time-Saving: Quick transactions without the need to visit a physical bank branch.
- Cost-Effective: Often lower fees for online transactions and services.
- Enhanced Security: Banks implement various security measures, such as encryption and two-factor authentication, to protect users’ data.
Security Measures
- Encryption: Sensitive data is encoded to prevent unauthorized access during transmission.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Requires users to verify their identity through a second method (e.g., SMS code, authenticator app).
- Secure Socket Layer (SSL): Ensures secure connections between users and the bank’s website.
- Fraud Detection: Banks employ systems to monitor and flag suspicious transactions.
Challenges of E-Banking
- Cyber security Risks: Threats such as phishing, malware, and hacking can compromise account security.
- Technical Issues: System outages or technical glitches may temporarily disrupt access to services.
- Digital Divide: Not all individuals have equal access to technology or the internet, which can limit e-banking adoption.
FOREIGN EXCHANGE TRANSACTIONS AND TRADE FINANCE
Banking system provides various forms of trade finance that helps facilitate import and export business. There are three main types of trade finance:
- Letters Of Credit (LC)
- Standby Letter Of Credit (SBLC)
- Buyer’s Credit
- Foreign Bank Guarantee
- LETTER OF CREDIT (LC)
A Letter of Credit (LC) is a financial document issued by a bank, guaranteeing that a buyer’s payment to a seller will be received on time and for the correct amount. LC is a vital instrument in international trade, providing security and facilitating transactions between buyers and sellers.
Process: The issuing bank ensures that payment will be made if the seller fulfills the terms agreed upon in the LC contract, such as delivering goods and services as specified
Key Features of a Letter of Credit
- Parties Involved:
- Applicant: The buyer (importer) who requests the LC from their bank.
- Beneficiary: The seller (exporter) who receives the payment.
- Issuing Bank: The bank that issues the LC on behalf of the buyer.
- Advising Bank: The bank that advises the beneficiary about the LC, usually located in the beneficiary’s country.
- Documents Required:
- To receive payment, the beneficiary must present specific documents, which may include:
- Bill of lading
- Commercial invoice
- Insurance certificate
- Packing list
- Any additional documents specified in the LC.
- Payment Guarantee:
- The LC guarantees that as long as the beneficiary presents the required documents that comply with the terms of the LC, the issuing bank will make the payment.
- Conditions and Terms:
- The LC will specify the conditions under which the payment will be made, including the timeframe for document submission and any specific requirements related to the shipment of goods.
Benefits of Using a Letter of Credit
- Security for Sellers: Provides assurance of payment once the terms are met, reducing the risk of non-payment.
- Risk Mitigation for Buyers: Buyers can ensure that payment is only made when the seller fulfills their obligations, such as shipping the goods.
- Facilitates International Trade: Helps establish trust between parties who may not know each other, especially in cross-border transactions.
Risks and Considerations
- Document Discrepancies: If the documents presented do not match the terms of the LC, payment may be delayed or denied.
- Costs: There are fees associated with issuing and processing an LC, which can add to transaction costs.
- Complexity: Understanding the requirements and terms of an LC can be complicated, necessitating careful attention to detail.
Types of Letters of Credit:
•Revocable vs. Irrevocable:
- Revocable: Can be amended or canceled by the issuing bank without notice to the beneficiary.
- Irrevocable: Cannot be changed or canceled without the consent of all parties.
Sight vs. Time:
- Sight: Payment is made immediately upon presentation of the required documents.
- Time: Payment is made at a later date, typically after a specified period.
•Confirmed LC: Another bank guarantees payment in addition to the issuing bank.
•Standby LC: This is a secondary payment method if the buyer fails to make payment.
STANDBY LETTER OF CREDIT (SBLC)
A Standby Letter of Credit (SBLC) is a financial instrument issued by a bank to guarantee payment to a beneficiary in the event that the applicant fails to fulfill their contractual obligations. In Standby L/C the importer’s bank makes a payment only if its customer fails to fulfill their obligations (i.e., in case of default). Therefore, the standby L/Cs issued by the importer’s bank obligates that bank to compensate the exporter only in the event of a performance failure. The importer will obviously pay a fee for this service and will be liable to its bank for any payments made by the bank under the standby L/C. Here’s an overview of SBLCs, including their features, uses, and benefits:
Key Features of Standby Letters of Credit
- Guarantee of Payment:
- The SBLC acts as a backup payment method, ensuring that the beneficiary receives payment if the applicant defaults on their obligations.
- Conditions for Payment:
- The beneficiary must present specific documents to the issuing bank that prove the applicant has failed to meet their obligations, such as invoices or contracts.
- Types of SBLCs:
- Performance SBLC: Guarantees the performance of contractual obligations.
- Financial SBLC: Ensures payment for financial transactions, such as loans or debts.
- Expiration Date:
- SBLCs typically have an expiration date, after which they are no longer valid.
- Transferability:
- Some SBLCs can be transferred to another party, providing flexibility in transactions.
Uses of Standby Letters of Credit
- International Trade:
- Commonly used in international transactions where trust between parties may be low. An SBLC provides assurance to the seller.
- Construction Contracts:
- Used to guarantee performance and completion of projects by contractors.
- Lease Agreements:
- Often required in lease agreements to ensure rent payments or property maintenance.
- Loan Transactions:
- Banks may request an SBLC from borrowers to guarantee repayment of loans.
Benefits of Standby Letters of Credit
- Risk Mitigation:
- Reduces the risk for sellers and lenders by ensuring payment in case of non-performance.
- Increased Credibility:
- Helps businesses enhance their creditworthiness, especially for new or less established companies.
- Facilitates Financing:
- Allows for smoother negotiations and transactions, as parties have a security net in place.
- Flexibility:
- Can be tailored to meet the specific needs of the transaction and the parties involved.
Process of Obtaining a Standby Letter of Credit
- Application: The applicant approaches their bank with a request for an SBLC, providing necessary documentation about the transaction.
- Credit Assessment: The bank evaluates the applicant’s creditworthiness and the nature of the transaction.
- Issuance: Once approved, the bank issues the SBLC, which outlines the terms and conditions.
- Use in Transaction: The applicant provides the SBLC to the beneficiary as part of the contractual agreement.
- Claim Process: If the applicant defaults, the beneficiary can claim payment by presenting the required documents to the issuing bank.
BUYER’S CREDIT
Buyers credit is a loan facility while letter of credit is a promise given by a bank to the seller that payment will be received on time. If the buyer cannot pay, the bank will be responsible for the entire amount of the purchase. Buyer’s credit is a credit facility available to importers from a foreign lender. This is usually a foreign bank or institution in the exporting country.One of the main advantages of using buyer’s credit instead of a normal LC is that the borrower wants the funding in foreign currency so that the importer can make payments to the exporter on time and in the currency of the exporter’s country.
What is the difference between letter of credit and buyer’s credit?
The fundamental difference between LC and buyer’s credit is that buyer’s credit is a loan that an importer takes and LC is a payment guarantee that an exporter uses.
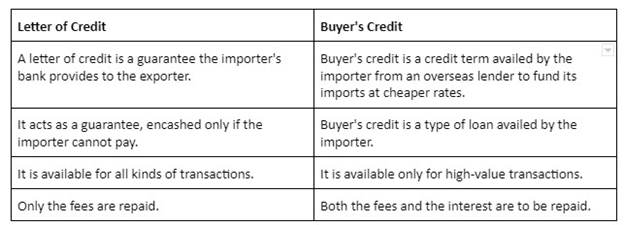
It is important to note that in practice buyer’s credit may be issued on the basis of a letter of credit. This shows that structurally the two products are completely different.
FOREIGN BANK GUARANTEE
A foreign bank guarantee is a financial instrument issued by a bank in one country to provide a guarantee on behalf of a client (the applicant) to a beneficiary in another country. This instrument serves as a promise that the bank will fulfill a financial obligation if the applicant defaults on their commitments.
Key Features of Foreign Bank Guarantees
- Types of Guarantees:
- Performance Guarantee: Ensures the applicant completes a project or service as agreed.
- Financial Guarantee: Ensures payment of a specified amount, often used in loans and credit transactions.
- Advance Payment Guarantee: Protects the beneficiary if the applicant fails to refund an advance payment.
- Cross-Border Transactions:
- Facilitates international trade by providing assurance to foreign suppliers or service providers.
- Risk Mitigation:
- Reduces the risk for beneficiaries, allowing them to engage with foreign clients with greater confidence.
- Documentation:
- Typically requires documentation like contracts, invoices, and proof of the financial obligation.
Process of Obtaining a Foreign Bank Guarantee
- Application:
- The applicant approaches a bank to request a guarantee, providing relevant documentation about the transaction or contract.
- Credit Assessment:
- The bank evaluates the applicant’s creditworthiness and the nature of the guarantee.
- Issuance:
- Once approved, the bank issues the guarantee, outlining the terms and conditions, including the amount and duration.
- Notification:
- The bank notifies the beneficiary of the guarantee, specifying the terms under which it can be claimed.
- Claim Process:
- If the applicant defaults, the beneficiary can claim payment by presenting required documents to the issuing bank.
Benefits of Foreign Bank Guarantees
- Enhanced Credibility:
- Increases the credibility of the applicant in international transactions.
- Facilitates Trade:
- Encourages international trade by reducing perceived risks for foreign partners.
- Flexibility:
- Can be tailored to specific transactions and requirements.
- Legal Protection:
- Provides legal assurance to the beneficiary, as the guarantee is a formal obligation of the bank.
